What Is Keto?
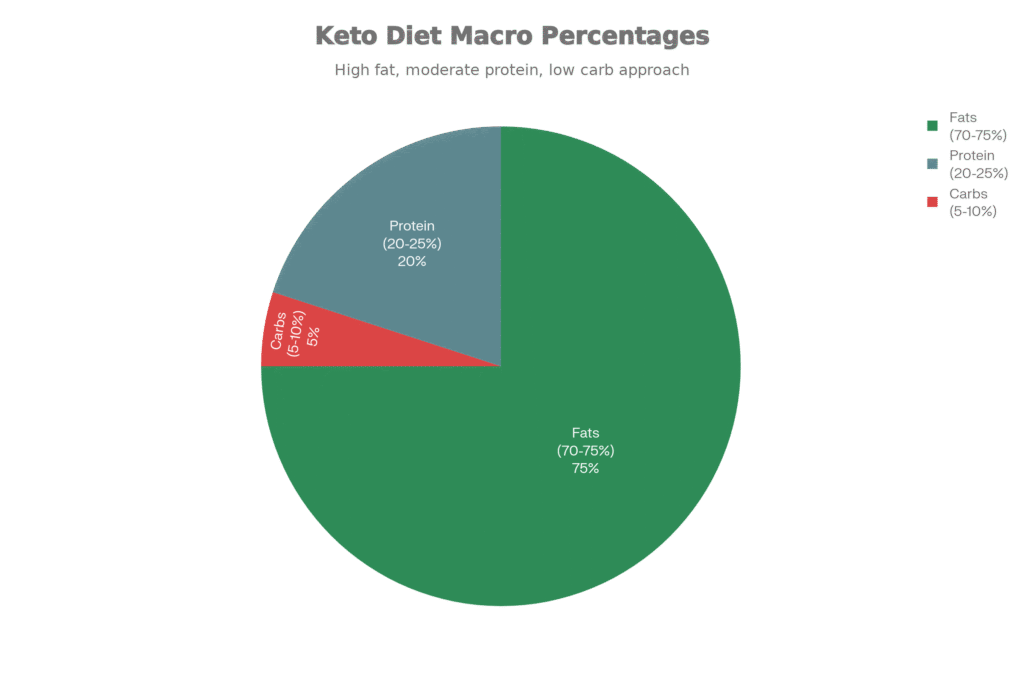
The ketogenic diet, or keto, is a high-fat, low-carb eating plan that shifts your body into ketosis—burning fat for fuel instead of carbs. Limit carbs to under 50 g daily (often 20-30 g net), moderate protein, and load up on healthy fats like avocados, nuts, olive oil, and fatty fish for about 70-75% of calories. This triggers the liver to produce ketones, delivering steady energy, weight loss, sharper focus, and benefits for hormonal health like PCOS
Note: If you’re struggling to see results on keto, you’re not alone. When I started my journey to lose 40 kg with PCOS, I realized that generic advice doesn’t work for hormonal weight loss. I’ve put together a complete, step-by-step [2026 Keto Guide] that reveals the exact protocol I used to reset my metabolism and balance my hormones naturally. Make sure to read it alongside this post to fast-track your results!
What Are Ketones?
Ketones are powerhouse molecules your liver produces from fats during low-carb states like the ketogenic diet or fasting, acting as a clean superfuel for your body and brain. The main types—acetoacetate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone—form via ketogenesis when carbs run low, letting your body burn stored fat instead of glucose for steady energy. These ketone bodies cross the blood-brain barrier efficiently, fueling up to 70% of brain needs for sharp focus and mental clarity without sugar crashes.
| Category | Top Keto Foods | Why It Fits Keto |
|---|---|---|
| Fats (70-75%) | Avocado, olive oil, butter, coconut oil, nuts (macadamia, almonds), cheese | Main superfuel source; keeps you full and drives ketogenesis. |
| Proteins (20-25%) | Eggs, fatty fish (salmon), chicken thighs, beef, bacon, pork rinds | Builds muscle without spiking carbs; moderate portions are key. |
| Carbs/Veggies (5-10%) | Broccoli, spinach, cauliflower, zucchini, asparagus, berries (limited) | Low-net-carb greens for fibre and nutrients under 20-50 g/day. |
How are ketones beneficial in keto?
Ketones shine in ketosis, curbing hunger, stabilising blood sugar, and boosting fat loss while reducing inflammation—ideal for women’s health issues like PCOS. Unlike glucose, ketones generate more ATP per oxygen molecule, earning their superfuel status for endurance and recovery on keto. Track ketone levels with strips or breath tests to confirm you’re in ketosis and reaping these perks.

What is the ketogenic state?
The Ketogenic State: The Shift to Lipid-Based Energy
The ketogenic state, often called “keto,” happens when your body switches from burning carbs for energy to using fats instead. Normally, you rely on glucose from sugars and starches, but in keto—triggered by a very low-carb, high-fat diet—your liver converts stored fats into ketones. These ketones become your brain and muscles’ main fuel source after a few days of adaptation.
This shift offers benefits like steady energy without sugar crashes, reduced hunger, and potential weight loss by tapping into fat reserves. It’s like upgrading from a finicky gas engine to a smooth diesel one—more efficient for endurance. Many report sharper focus once adapted, though initial “keto flu” fatigue is common as your body adjusts.
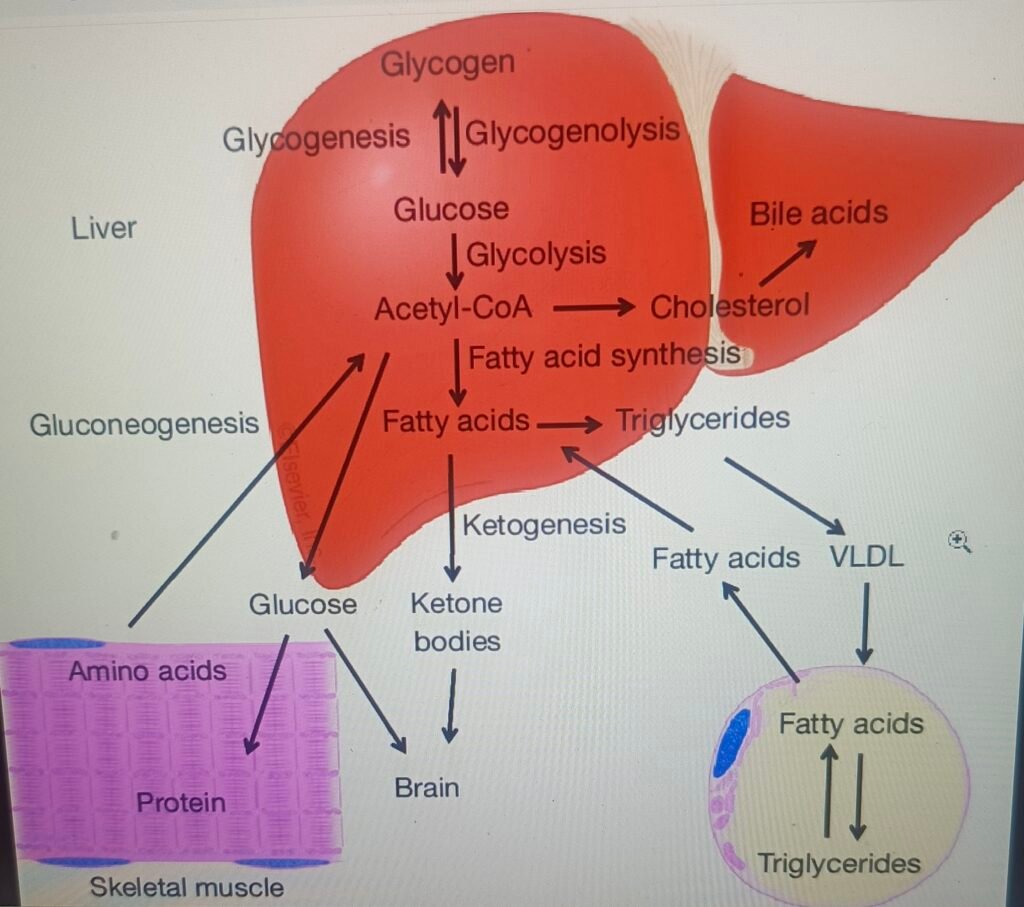
Ketogenesis: The Liver’s Synthesis
Ketogenesis is the liver’s clever process of turning fats into ketone bodies, your body’s backup fuel when carbs are scarce. This fat-to-fuel magic keeps energy steady during fasting or keto diets. Ketogenesis liver synthesis powers the ketogenic diet by converting fats into ketones right in your liver’s mitochondria—connecting directly to the keto foods chart above. When you eat high-fat foods like avocados and olive oil while keeping carbs low, fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation to form acetyl-CoA, and then HMG-CoA synthase crafts ketone bodies for clean superfuel. This ketogenesis liver synthesis ensures steady energy during keto-adaptation, fuelling your brain past the blood-brain barrier and tapping fat stores for weight loss and hormonal balance. (This information is taken from the World Health Organization).
Why are ketones a “superfuel”?
When your body taps into ketones during ketosis, it unlocks a superfuel that revolutionises cellular energy like nothing else. Unlike glucose, which burns quickly and leaves you crashing, ketones—produced by the liver through ketogenesis—deliver a steady stream of ATP, the cell’s energy currency. This superfuel efficiency comes from how ketones feed directly into the mitochondria, generating up to 30% more energy per unit of oxygen compared to carbs. No wonder athletes and keto fans rave about sustained stamina without the midday slump.
The Brain and the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
Ketones crossing the blood-brain barrier efficiently fuel the brain during ketosis. The BBB acts as a tight protective filter but lets ketones pass quickly via MCT1 transporters—unlike insulin-dependent glucose. This supplies up to 70% of brain energy, sharpening focus and clearing fog without carb crashes.
BBB’s role in ketone brain energy delivery keeps cognition steady and clean. Ketones crossing the blood-brain barrier efficiently cut inflammation and boost neurone protection, aiding memory and mood—key for keto benefits in hormonal health.
What is the timeline for “keto-adaptation”
The keto-adaptation timeline unfolds over 2-8 weeks as your body shifts from carb-burning to fat-fuelled ketosis on the ketogenic diet. Days 1-3 deplete glycogen stores, sparking initial ketone production but often bringing “keto flu” fatigue—combat it with electrolytes like sodium and magnesium.
Stages of the keto adaptation process ramp up next: Weeks 1-2 stabilise energy as the liver ramps up ketogenesis; by weeks 3-6, muscles and the brain embrace ketones for cleaner superfuel, boosting focus and endurance. The full keto-adaptation timeline hits at 6-8 weeks, unlocking fat loss, steady vitality, and blood-brain barrier efficiency for mental sharpness—perfect for PCOS and hormonal balance.
Have A Question? If any, drop in the comment box!
How long does it take to enter ketosis?
Most individuals enter nutritional ketosis within 24 to 72 hours of strict carbohydrate restriction. However, becoming “fat-adapted”—where the body efficiently utilises fat as its primary fuel source for physical performance—can take 4 to 6 weeks.
Does the ketogenic diet cause muscle loss?
No, provided protein intake is adequate. Ketones, specifically beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB), have a protein-sparing effect. In a state of ketosis, the body uses fat and ketones for energy instead of breaking down muscle tissue for gluconeogenesis.
Is keto safe for long-term use?
Current clinical research (as of 2026) suggests that well-formulated ketogenic diets are safe for most healthy individuals. However, long-term practitioners should monitor lipid profiles and liver enzymes, as extreme saturated fat intake can affect individuals differently based on their genetics (e.g., APOE4 carriers).
The Science of Ketosis:
The science of ketosis reveals how a low-carb ketogenic diet triggers the liver to ramp up ketogenesis, converting fatty acids into ketone bodies like beta-hydroxybutyrate via beta-oxidation and HMG-CoA pathways when glucose is scarce. Low insulin unlocks fat stores, while hormones like glucagon boost this shift, making ketones the efficient superfuel that crosses the blood-brain barrier for steady brain energy during keto-adaptation.
Conclusion: Ketosis unlocks fat-burning power.
Mastering the science of ketosis empowers sustainable fat loss, mental sharpness, and hormonal balance on keto—transforming your body into a fat-burning machine beyond temporary diets.







4 Comments